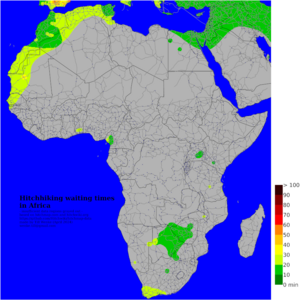
Africa
Hitching for rides is common practice in Africa, though you may be expected to pay the driver.
Road safety in Africa leaves a lot to be desired, and seatbelts are not always fitted. Being stranded in remote areas could be a problem. Speaking English and French is an advantage as well as Portuguese in some countries. However, learning the basic of African languages will make your trip much more pleasant. Some languages are understood in very large parts, such as Wolof, Fulfulde and Bambara in West Africa or Swahili and Arabic in Eastern Africa.
For Europeans and Americans visas in Africa are relatively hard compared to other continents. For most countries it's a good idea to plan ahead.
Health
Malaria is common in most parts of Africa. Inform yourself and take precautions. Some forms of malaria are particularly deadly. The fact that local populations don't take any malaria prophelactics should definitely not stop you from taking any: locals are much more resistant to malaria.
Countries
The United Nations Statistics Division defines Africa as following:
Northern Africa
Eastern Africa
 Burundi
Burundi Comoros
Comoros Djibouti
Djibouti Eritrea
Eritrea Ethiopia
Ethiopia Kenya
Kenya Madagascar
Madagascar Malawi
Malawi Mauritius
Mauritius Mozambique
Mozambique Rwanda
Rwanda Seychelles
Seychelles Somalia
Somalia Uganda
Uganda United Republic of Tanzania
United Republic of Tanzania Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Central Africa
 Angola
Angola Cameroon
Cameroon Central African Republic
Central African Republic Chad
Chad Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Gabon
Gabon Sao Tome and Principe
Sao Tome and Principe
Southern Africa
Western Africa
 Benin
Benin Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Cape Verde
Cape Verde Cote d'Ivoire
Cote d'Ivoire Gambia
Gambia Ghana
Ghana Guinea
Guinea Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Liberia
Liberia Mali
Mali Mauritania
Mauritania Niger
Niger Nigeria
Nigeria Senegal
Senegal Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Togo
Togo